OVERVIEW
Qualia NAD+® significantly increased NAD+ levels in healthy adults compared to placebo (p < 0.001) in a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. There was an average increase of 67% in NAD+ after taking Qualia NAD+ once daily for 4 weeks. Females taking NAD+ also saw improvements in aging symptoms in the “overall” and “somatic” (general well-being, sleep, feelings of exhaustion, etc.) categories compared to placebo (p = 0.03 for both).*
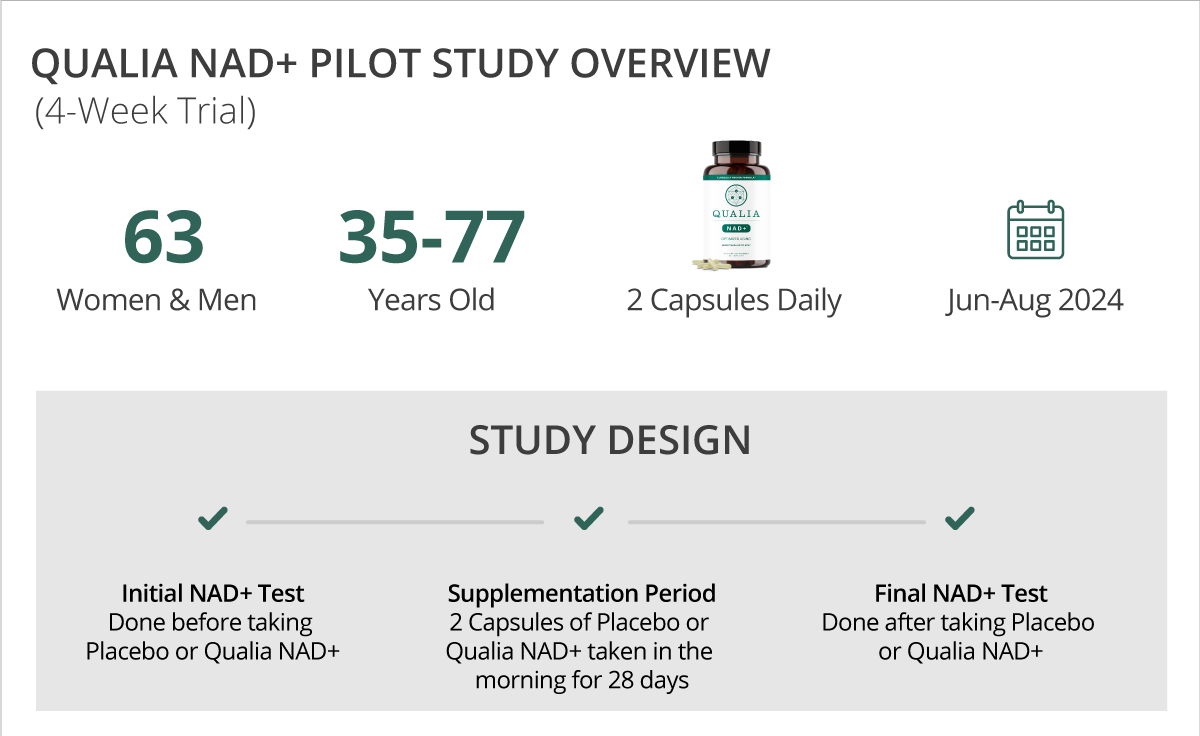
HOW THE STUDY IS DESIGNED
There were two groups in the study: one took Qualia NAD+ capsules and the other took placebo capsules. Participants were randomly assigned to be in one of the two groups.
The study was double-blinded, which means that neither the researchers conducting the study nor the participants knew who received Qualia NAD+ or placebo capsules until after the participants had completed the study protocol.
Participants took either Qualia NAD+ or a placebo daily for 28 days. The instructions were to take two capsules every day anytime in the morning, with or without food.
The primary study endpoint was the change in NAD+ levels, which was determined by comparing initial and final NAD+ blood levels using at-home, self-administered finger stick kits.
Secondary endpoints were assessed using questionnaires that included a general health survey (RAND-SF-36) and male and female versions of a questionnaire that asked about common health challenges associated with aging.
RESULT
Qualia NAD+ Increased NAD+ Levels by an Average of 67%*
 The study was conducted between June and August 2024. A group of 170 healthy adults were voluntarily recruited and sent at-home finger stick blood kits to measure initial blood NAD+ levels prior to beginning the study protocol.
The study was conducted between June and August 2024. A group of 170 healthy adults were voluntarily recruited and sent at-home finger stick blood kits to measure initial blood NAD+ levels prior to beginning the study protocol.
One hundred and two (102) participants successfully completed the initial test to obtain their baseline NAD+ measurements and were instructed to take Qualia NAD+ or placebo. Sixty-three (63) of the 175 participants successfully completed both the initial test and a second NAD+ test after taking Qualia NAD+ or a placebo for 28 days. NAD+ data analysis is based on these 63 participants who had both initial and final NAD+ measurements. These participants ranged from 35 to 77 years old, with an average age of 54.2 years. Participants were a mix of females (N = 39) and males (N = 24).
The average increase in whole blood NAD+ levels from baseline was 67% in the participants taking Qualia NAD+ and was 4% in the participants taking the placebo. The increase in NAD+ levels in participants taking Qualia NAD+ was statistically significant compared to their baseline levels and compared to placebo (p < 0.001). These results were consistent with the data from our first placebo-controlled study, where the group receiving Qualia NAD+ had a greater increase in NAD+ levels than the placebo group (Qualia NAD+ = 74%, Placebo = 4%; p < 0.001) [1].*
The NAD+ increase of 67% found in this study is greater than what has been reported to occur with a similar amount of nicotinamide riboside given alone [2], indicating that the comprehensive approach taken by Qualia NAD+, which combines nicotinamide riboside with two additional NAD+ precursors and other ingredients intended to support the making of NAD+, has additive benefits and is more effective than nicotinamide riboside given alone.*
Note: The most common reasons for failing to successfully complete NAD+ measurements were: (1) failure to send in the initial or final at-home finger stick blood kits to the lab for analysis, (2) insufficient blood sample of the submitted test kit, and (3) too much time having elapsed between when the sample was collected and returned to the lab.
Females Taking Qualia NAD+ Had Improvements in Subjective Symptoms Related to Healthy Aging*
The Aging Female Symptom (AFS) scale asks about common health challenges that occur with aging in females. This scale produces an overall score, and subscores for psychological (irritability, mood, nervousness, etc.), somatic (general well-being, sleep, feelings of exhaustion, etc), and sexual health. Lower scores on the AFS indicate healthier aging, and a decrease in scores from baseline to the end of the study suggests improvements in psychological, physical, or sexual health may have occurred.*
Fifty-one (51) of the female participants completed an AFS scale at baseline and after 28 days of taking Qualia NAD+ or placebo. Scores in the NAD+ group significantly improved from baseline compared to the placebo group. Specifically, overall score (Qualia NAD+ = 20.7% improvement, Placebo = 10.8% improvement, p = 0.03)and somatic score (Qualia NAD+ = 22.2% improvement Placebo = 10.6% improvement, p = 0.03) improved.*
Males Taking Qualia NAD+ Did Not Have Improvements in Subjective Symptoms Related to Healthy Aging*
Similar to the AFS, the Aging Male Symptom (AMS) scale asks about common health challenges that occur with aging in males, and produces an overall score and subscores for psychological, somatic, and sexual health. Forty (40) of the male participants completed an AMS scale at baseline and after 28 days of taking Qualia NAD+ or placebo. None of the changes in the Qualia NAD+ group were statistically significant compared to the placebo group.*
All Participants Taking Qualia NAD+ Had Improvements in Vitality and Emotional Well-Being*
The 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36) was developed by RAND as part of the Medical Outcomes Study (MOS). Questions are grouped into eight subscales intended to assess physical functioning, muscle and joint discomfort, role limitations due to physical health problems, role limitations due to personal or emotional problems, emotional well-being, social functioning, energy/fatigue, and general health perceptions. It also includes a single item that provides an indication of perceived change in health. It is one of the most widely used general health questionnaires.*
Ninety participants completed the SF-36 at baseline and after 28 days. Improvement was greater in the Qualia NAD+ group than in the placebo group for vitality on days 21 and 28 (Day 28 stats: Qualia NAD+ = 20.4% improvement, Placebo = 10.7% improvement, p < 0.01) and emotional well-being on days 14, 21, and 28 (Day 28 stats: Qualia NAD+ = 10.4% improvement, placebo = 1.4% improvement, p < 0.01).*
1. Qualia NAD+ Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study Results." Qualia Life. Available at: https://www.qualialife.com/studies/qualia-nad-placebo-controlled-clinical-study. (Accessed: 21 November 2024)
2. Conze D, Brenner C, Kruger CL. Safety and Metabolism of Long-term Administration of NIAGEN (Nicotinamide Riboside Chloride) in a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial of Healthy Overweight Adults. Sci Rep. 2019;9: 9772. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-46120-z
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. The products and information on this website are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. The information on this site is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please speak with an appropriate healthcare professional when evaluating any wellness related therapy. Please read the full medical disclaimer before taking any of the products offered on this site.


Charles Brandon Theis